分类: 未分类
密码保护:armbian安装supervised版本home assistant
在ubuntu上安装supervised ha的另一种方案(未经检验)
密码保护:调整img文件大小
手动扩展空间
扩展SD卡/eMMC上的空间 – 恩智浦8MMNAVQ:NavQ配套计算机 (gitbook.io)
手动扩展空间
如果不想使用该脚本,可以运行以下命令。
安装 ROS 时,您可能会遇到 eMMC 或 SD 卡空间不足的问题。若要展开 rootfs 分区,请按照下列步骤操作:
如果您在 eMMC 上,您将使用 /dev/mmcblk2。如果您使用的是 SD 卡,请使用 /dev/mmcblk1。默认情况下,NavQ 从套件中随附的 SD 卡启动。
$ sudo fdisk /dev/mmcblk1
Command (m for help): p
Device Boot Start End Blocks Size Id System
/dev/mmcblk1p1 * 16384 186775 170392 83.2M c W95 FAT32 (LBA)
/dev/mmcblk1p2 196608 <end> <blocks> <size> 83 Linux
Command (m for help): d
Partition number (1,2, default 2): 2
Partition 2 has been deleted.
Command (m for help): p
Device Boot Start End Blocks Size Id System
/dev/mmcblk1p1 * 16384 186775 170392 83.2M c W95 FAT32 (LBA)
Command (m for help): n
Partition type
e extended
p primary partition (1-4)
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 2
First sector (2048-30621695, default 2048): 196608
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-30621695, default 30621695): <press enter for default>
Created a new partition 2 of type ‘Linux’ and of size 14.5 GiB.
Partition #2 contains a ext4 signature.
Do you want to remove the signature? [Y]es/[N]o: n
Command (m for help): p
Device Boot Start End Blocks Size Id System
/dev/mmcblk1p1 * 16384 186775 170392 83.2M c W95 FAT32 (LBA)
/dev/mmcblk1p2 196608 30621695 39425088 14.5G 83 Linux
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
完成这些步骤后,请运行以下命令:
$ sudo resize2fs /dev/mmcblk1p2
并重新启动。您现在应该能够安装 ROS Melodic 而不会出现大小问题。
fdisk 的命令
如果您只想查看命令,这些是您需要在 fdisk 中运行的命令,以便调整磁盘大小。
d <enter>
2 <enter>
n <enter>
p <enter>
2 <enter>
196608 <enter>
<enter>
n <enter>
w <enter>
<fdisk should exit>
$ sudo resize2fs /dev/mmcblk2p2 <enter> (FOR eMMC)
$ sudo resize2fs /dev/mmcblk1p2 <enter> (FOR SD CARD)
armbian下压缩磁盘镜像包
dedalodaelus/ArmbianShrink:让你的 armbian 图像更小! (github.com)
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dedalodaelus/ArmbianShrink/master/armbianshrink.sh
chmod +x armbianshrink.sh
sudo mv armbianshrink.sh /usr/local/bin
[user@localhost ArmbianShrink]$ sudo armbianshrink.sh armbian.img
e2fsck 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Pass 1: Checking inodes, blocks, and sizes
Pass 2: Checking directory structure
Pass 3: Checking directory connectivity
Pass 4: Checking reference counts
Pass 5: Checking group summary information
/dev/loop1: 88262/1929536 files (0.2% non-contiguous), 842728/7717632 blocks
resize2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
resize2fs 1.42.9 (28-Dec-2013)
Resizing the filesystem on /dev/loop1 to 773603 (4k) blocks.
Begin pass 2 (max = 100387)
Relocating blocks XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Begin pass 3 (max = 236)
Scanning inode table XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
Begin pass 4 (max = 7348)
Updating inode references XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
The filesystem on /dev/loop1 is now 773603 blocks long.
Shrunk armbian.img from 30G to 3.1Gsudo armbianshrink.sh [-s] imagefile.img [newimagefile.img]dedalodaelus/ArmbianShrink: Make your armbian images smaller! (github.com)
tailscal
密码保护:home automation supervised安装及os-agent 文件
树莓派磁盘操作命令
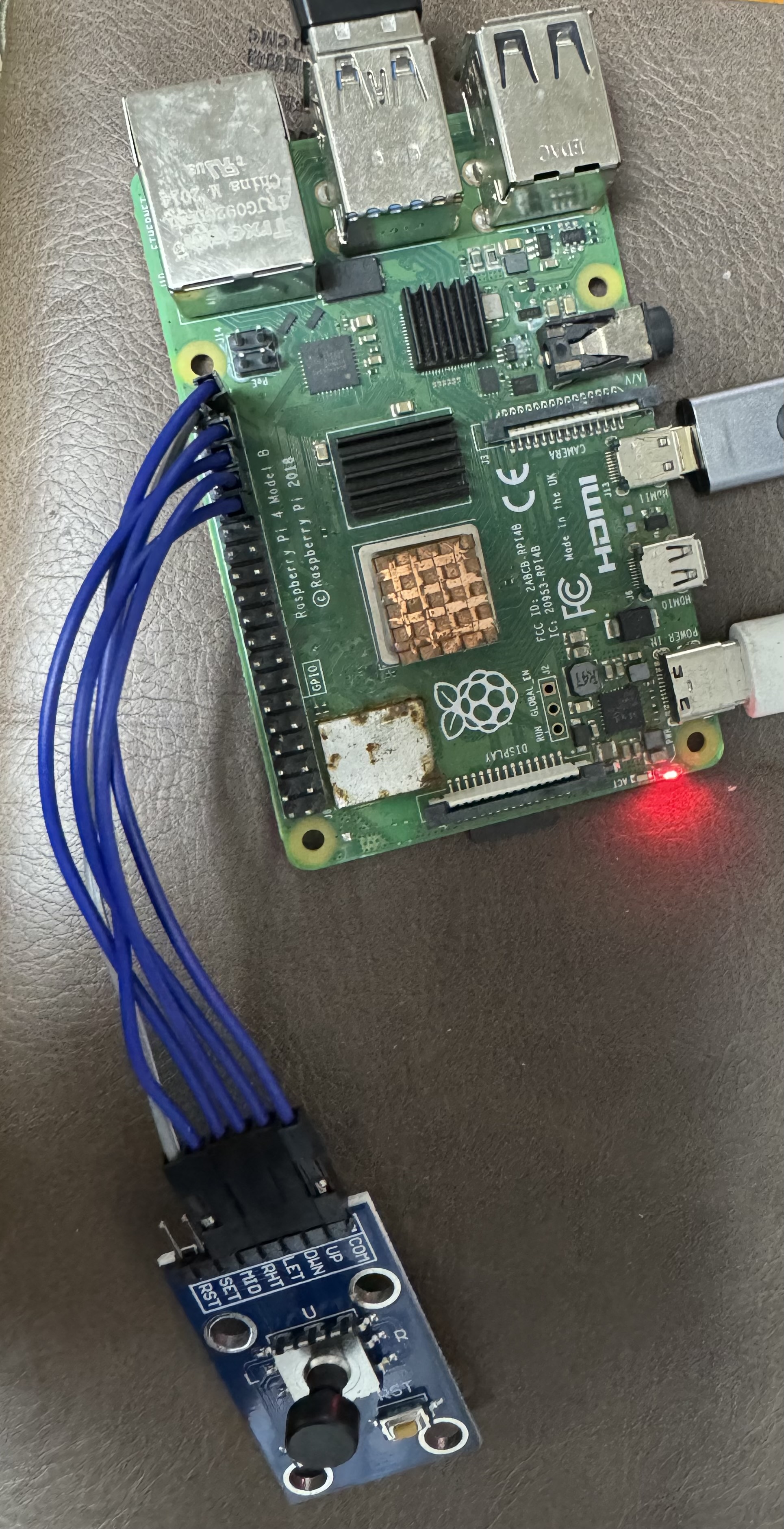
树莓派上基于Python编写按键驱动程序
import multiprocessing
import time
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import uinput
# 初始化输入GPIO引脚,将引脚拉低
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # 使用BCM方式编号
up_pin = 5 # 可对照前文中管脚编号定义
down_pin = 6
left_pin = 13
right_pin = 19
left_button_pin = 20
right_button_pin = 12
GPIO.setup(up_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # 将管脚均设置为输入上拉模式
GPIO.setup(down_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(left_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(right_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(left_button_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(right_button_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
# 创建虚拟输入设备(鼠标)
device = uinput.Device([uinput.BTN_LEFT, uinput.BTN_RIGHT, uinput.REL_X, uinput.REL_Y])
XY_STEP = 1 # 用于调节光标的移动步长
# 定义一个通用四向摇杆按键操作的进程处理函数
def direction_key_process(queue, pin, direction):
while True:
GPIO.wait_for_edge(pin, GPIO.BOTH) # 该进程Pending等待四向摇杆按键发生动作
while GPIO.input(pin) == direction: # 如果是有效的低电平,那么它将持续向队列写入管脚编号
queue.put(pin)
time.sleep(0.005) # 此延迟可调节光标灵敏度
# 定义一个通用处理左右按键操作的进程
def leftright_key_process(queue, pin):
while True:
GPIO.wait_for_edge(pin, GPIO.BOTH) # 该进程Pending等待左/右按键发生动作
queue.put(pin) # 一旦有状态变化,则将按键编号写入队列
# 定义一个更新光标位置的进程处理函数
def update_position_device():
while True:
pin = position_queue.get() # 该进程Pending等待方向按键队列数据
if pin == up_pin:
device.emit(uinput.REL_Y, -XY_STEP) # 根据按键方向移动光标XY轴位置
elif pin == down_pin:
device.emit(uinput.REL_Y, XY_STEP)
elif pin == left_pin:
device.emit(uinput.REL_X, -XY_STEP)
elif pin == right_pin:
device.emit(uinput.REL_X, XY_STEP)
# 定义一个更新左右按钮状态的进程处理函数
def update_button_device():
while True:
pin = button_queue.get() # 该进程Pending等待左右按键队列数据
if pin == left_button_pin:
if GPIO.input(pin) == GPIO.LOW:
device.emit(uinput.BTN_LEFT, 1) # 按键按下
else:
device.emit(uinput.BTN_LEFT, 0) # 按键释放
elif pin == right_button_pin:
if GPIO.input(pin) == GPIO.LOW:
device.emit(uinput.BTN_RIGHT, 1)
else:
device.emit(uinput.BTN_RIGHT, 0)
# 为方向按键、左右建分别创建一个队列来保存按键操作的引脚
position_queue = multiprocessing.Queue()
button_queue = multiprocessing.Queue()
# 创建多个进程来处理按键和按钮事件(每个按钮一个进程,互不影响)
processes = [
multiprocessing.Process(target=direction_key_process, args=(position_queue, up_pin, GPIO.LOW)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=direction_key_process, args=(position_queue, down_pin, GPIO.LOW)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=direction_key_process, args=(position_queue, left_pin, GPIO.LOW)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=direction_key_process, args=(position_queue, right_pin, GPIO.LOW)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=leftright_key_process, args=(button_queue, left_button_pin)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=leftright_key_process, args=(button_queue, right_button_pin))
]
# 启动所有进程
for p in processes:
p.daemon = True # 设置为守护进程,即在主进程结束时自动结束
p.start()
# 启动两个进程来更新设备状态
update_position_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=update_position_device)
update_position_process.daemon = True # 设置为守护进程,即在主进程结束时自动结束
update_position_process.start()
update_button_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=update_button_device)
update_button_process.daemon = True # 设置为守护进程,即在主进程结束时自动结束
update_button_process.start()
# 等待所有进程结束
for p in processes:
p.join()
update_position_process.join()
update_button_process.join()如果运行错误,请执行如下指令
lsmod | grep uinput
sudo modprobe uinputhttp://www.etrd.org/2023/05/14/%E6%A0%91%E8%8E%93%E6%B4%BE%E4%B8%8A%E5%9F%BA%E4%BA%8EPython%E7%BC%96%E5%86%99%E6%8C%89%E9%94%AE%E9%A9%B1%E5%8A%A8%E7%A8%8B%E5%BA%8F/
https://www.cnpython.com/qa/1003180
以下是正常代码
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
from sys import version_info
import uinput
device = uinput.Device([
uinput.KEY_LEFTSHIFT,
uinput.KEY_TAB,
uinput.KEY_SPACE,
uinput.KEY_LEFTALT
])
if version_info.major == 3:
raw_input = input
# Set up pins
# Rotary A Pin
RoAPin = 17
# Rotary B Pin
RoBPin = 18
# Rotary Switch Pin
RoSPin = 27
def print_message():
print ("========================================")
print ("| Rotary Encoder |")
print ("| ------------------------------ |")
print ("| Pin A connect to GPIO17 |")
print ("| Pin B connect to GPIO18 |")
print ("| Button Pin connect to GPIO27 |")
print ("| |")
print ("| Use a Rotary Encoder |")
print ("| Rotary to add/minus counter |")
print ("| Press to set counter to 0 |")
print ("| |")
print ("| SunFounder|")
print ("========================================\n")
print ("Program is running...")
print ("Please press Ctrl+C to end the program...")
#raw_input ("Press Enter to begin\n")
def setup():
global counter
global Last_RoB_Status, Current_RoB_Status
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(RoAPin, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(RoBPin, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(RoSPin,GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
# Set up a falling edge detect to callback clear
GPIO.add_event_detect(RoSPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=clear)
# Set up a counter as a global variable
counter = 0
Last_RoB_Status = 0
Current_RoB_Status = 0
# Define a function to deal with rotary encoder
def rotaryDeal():
global counter
global Last_RoB_Status, Current_RoB_Status
flag = 0
Last_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin)
# When RoAPin level changes
while(not GPIO.input(RoAPin)):
Current_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin)
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
# Reset flag
flag = 0
if (Last_RoB_Status == 0) and (Current_RoB_Status == 1):
counter = counter + 1
# time.sleep(0.5)
device.emit_combo([
# uinput.KEY_LEFTALT,
# uinput.KEY_LEFTALT,
uinput.KEY_TAB,
])
if (Last_RoB_Status == 1) and (Current_RoB_Status == 0):
device.emit_combo([
uinput.KEY_SPACE,
# uinput.KEY_TAB,
])
counter = counter - 1
print ("counter = %d" % counter)
# Define a callback function on switch, to clean "counter"
def clear(ev=None):
global counter
counter = 0
def main():
print_message()
while True:
rotaryDeal()
def destroy():
# Release resource
GPIO.cleanup()
# If run this script directly, do:
if __name__ == '__main__':
setup()
try:
main()
# When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program
# destroy() will be executed.
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
实现TAB/SHIFT+TAB键的前进后退
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
from sys import version_info
import uinput
device = uinput.Device([
uinput.KEY_LEFTSHIFT,
uinput.KEY_TAB,
uinput.KEY_SPACE,
uinput.KEY_LEFTALT
])
if version_info.major == 3:
raw_input = input
# Set up pins
# Rotary A Pin
RoAPin = 17
# Rotary B Pin
RoBPin = 18
# Rotary Switch Pin
RoSPin = 27
def print_message():
print ("========================================")
print ("| Rotary Encoder |")
print ("| ------------------------------ |")
print ("| Pin A connect to GPIO17 |")
print ("| Pin B connect to GPIO18 |")
print ("| Button Pin connect to GPIO27 |")
print ("| |")
print ("| Use a Rotary Encoder |")
print ("| Rotary to add/minus counter |")
print ("| Press to set counter to 0 |")
print ("| |")
print ("| SunFounder|")
print ("========================================\n")
print ("Program is running...")
print ("Please press Ctrl+C to end the program...")
#raw_input ("Press Enter to begin\n")
def setup():
global counter
global Last_RoB_Status, Current_RoB_Status
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(RoAPin, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(RoBPin, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(RoSPin,GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
# Set up a falling edge detect to callback clear
GPIO.add_event_detect(RoSPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=clear)
# Set up a counter as a global variable
counter = 0
Last_RoB_Status = 0
Current_RoB_Status = 0
# Define a function to deal with rotary encoder
def rotaryDeal():
global counter
global Last_RoB_Status, Current_RoB_Status
flag = 0
Last_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin)
# When RoAPin level changes
while(not GPIO.input(RoAPin)):
Current_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin)
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
# Reset flag
flag = 0
if (Last_RoB_Status == 0) and (Current_RoB_Status == 1):
counter = counter + 1
# time.sleep(0.5)
device.emit_combo([
# uinput.KEY_LEFTALT,
# uinput.KEY_LEFTALT,
uinput.KEY_TAB,
])
if (Last_RoB_Status == 1) and (Current_RoB_Status == 0):
device.emit_combo([
uinput.KEY_LEFTSHIFT,
uinput.KEY_TAB,
])
counter = counter - 1
# print ("counter = %d" % counter)
# Define a callback function on switch, to clean "counter"
def clear(ev=None):
global counter
counter = 0
def main():
print_message()
while True:
rotaryDeal()
def destroy():
# Release resource
GPIO.cleanup()
# If run this script directly, do:
if __name__ == '__main__':
setup()
try:
main()
# When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program
# destroy() will be executed.
except KeyboardInterrupt:
destroy()
一个正常运行的例子,可以移动光标并按下确定按钮
import multiprocessing
import time
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import uinput
# 初始化输入GPIO引脚,将引脚拉低
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # 使用BCM方式编号
up_pin = 5 # 可对照前文中管脚编号定义
down_pin = 6
left_pin = 13
right_pin = 19
left_button_pin = 20
right_button_pin = 12
GPIO.setup(up_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # 将管脚均设置为输入上拉模式
GPIO.setup(down_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(left_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(right_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(left_button_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
GPIO.setup(right_button_pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
# 创建虚拟输入设备(鼠标)
device = uinput.Device([uinput.BTN_LEFT, uinput.BTN_RIGHT, uinput.REL_X, uinput.REL_Y])
XY_STEP = 1 # 用于调节光标的移动步长
# 定义一个通用四向摇杆按键操作的进程处理函数
def direction_key_process(queue, pin, direction):
while True:
GPIO.wait_for_edge(pin, GPIO.BOTH) # 该进程Pending等待四向摇杆按键发生动作
while GPIO.input(pin) == direction: # 如果是有效的低电平,那么它将持续向队列写入管脚编号
queue.put(pin)
time.sleep(0.005) # 此延迟可调节光标灵敏度
# 定义一个通用处理左右按键操作的进程
def leftright_key_process(queue, pin):
while True:
GPIO.wait_for_edge(pin, GPIO.BOTH) # 该进程Pending等待左/右按键发生动作
queue.put(pin) # 一旦有状态变化,则将按键编号写入队列
# 定义一个更新光标位置的进程处理函数
def update_position_device():
while True:
pin = position_queue.get() # 该进程Pending等待方向按键队列数据
if pin == up_pin:
device.emit(uinput.REL_Y, -XY_STEP) # 根据按键方向移动光标XY轴位置
elif pin == down_pin:
device.emit(uinput.REL_Y, XY_STEP)
elif pin == left_pin:
device.emit(uinput.REL_X, -XY_STEP)
elif pin == right_pin:
device.emit(uinput.REL_X, XY_STEP)
# 定义一个更新左右按钮状态的进程处理函数
def update_button_device():
while True:
pin = button_queue.get() # 该进程Pending等待左右按键队列数据
if pin == left_button_pin:
if GPIO.input(pin) == GPIO.LOW:
device.emit(uinput.BTN_LEFT, 1) # 按键按下
else:
device.emit(uinput.BTN_LEFT, 0) # 按键释放
elif pin == right_button_pin:
if GPIO.input(pin) == GPIO.LOW:
device.emit(uinput.BTN_RIGHT, 1)
else:
device.emit(uinput.BTN_RIGHT, 0)
# 为方向按键、左右建分别创建一个队列来保存按键操作的引脚
position_queue = multiprocessing.Queue()
button_queue = multiprocessing.Queue()
# 创建多个进程来处理按键和按钮事件(每个按钮一个进程,互不影响)
processes = [
multiprocessing.Process(target=direction_key_process, args=(position_queue, up_pin, GPIO.LOW)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=direction_key_process, args=(position_queue, down_pin, GPIO.LOW)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=direction_key_process, args=(position_queue, left_pin, GPIO.LOW)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=direction_key_process, args=(position_queue, right_pin, GPIO.LOW)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=leftright_key_process, args=(button_queue, left_button_pin)),
multiprocessing.Process(target=leftright_key_process, args=(button_queue, right_button_pin))
]
# 启动所有进程
for p in processes:
p.daemon = True # 设置为守护进程,即在主进程结束时自动结束
p.start()
# 启动两个进程来更新设备状态
update_position_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=update_position_device)
update_position_process.daemon = True # 设置为守护进程,即在主进程结束时自动结束
update_position_process.start()
update_button_process = multiprocessing.Process(target=update_button_device)
update_button_process.daemon = True # 设置为守护进程,即在主进程结束时自动结束
update_button_process.start()
# 等待所有进程结束
for p in processes:
p.join()
update_position_process.join()
update_button_process.join()

主要代码都做了注释解释,其中关键几点是:
- 为每个按键都创建了一个进程(非线程),用于检测按键是否有动作;同时还为方向、左右键的动作更新到uinput分别创建了两个进程;使用了两个队列,来建立按键检测进程和uinput更新进程之间的数据通信。
- 所有进程都要配置为守护进程,使得主进程结束时,可以将所有进程同步结束,否则可能出现Python脚本已退出,但创建的进程还在运行的情况。
- 所有进程都使用Pending等待的方式等待事件发生(按键检测进程等待IO边沿发生,更新设备状态进程等待队列有数据),才执行代码,以便在无按键动作时尽可能不占用CPU资源
若开机自动运行该脚本,则可配置开机自启动。
可正常运行的旋转编码器版本
#!/usr/bin/env python
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import uinput
device = uinput.Device([
uinput.KEY_LEFTSHIFT,
uinput.KEY_TAB,
uinput.KEY_SPACE
])
RoAPin = 17 # CLK Pin
RoBPin = 18 # DT Pin
BtnPin = 27 # Button Pin
globalCounter = 0
flag = 0
Last_RoB_Status = 0
Current_RoB_Status = 0
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(RoAPin, GPIO.IN) # input mode
GPIO.setup(RoBPin, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(BtnPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
def rotaryDeal():
global flag
global Last_RoB_Status
global Current_RoB_Status
global globalCounter
Last_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin)
while(not GPIO.input(RoAPin)): #未旋转时,GPIO.input(RoAPin)值为1,旋转时会变为0
Current_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin) #旋转时的当前值
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
flag = 0
if (Last_RoB_Status == 1) and (Current_RoB_Status == 0):
globalCounter = globalCounter + 1 #顺时针旋转,角位移增大
device.emit_combo([uinput.KEY_LEFTSHIFT,uinput.KEY_TAB,])
if (Last_RoB_Status == 0) and (Current_RoB_Status == 1):
globalCounter = globalCounter - 1 #逆时针旋转,数值减小
device.emit_combo([uinput.KEY_TAB,])
def btnISR(channel):
global globalCounter
globalCounter = 0
device.emit_combo([uinput.KEY_SPACE,])
def loop():
global globalCounter
tmp = 0 # Rotary Temperary
GPIO.add_event_detect(BtnPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=btnISR)
#当按下按钮时,调用回调函数btnISR
while True:
rotaryDeal()
if tmp != globalCounter:
print('globalCounter = %d' % globalCounter)
tmp = globalCounter
def destroy():
GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()
sudo nano /etc/rc.local
# rc.local
#
# This script is executed at the end of each multiuser runlevel.
# Make sure that the script will "exit 0" on success or any other
# value on error.
#
# In order to enable or disable this script just change the execution
# bits.
#
# By default this script does nothing.
# Print the IP address
_IP=$(hostname -I) || true
if [ "$_IP" ]; then
printf "My IP address is %s\n" "$_IP"
fi
sudo modprobe uinput
sudo /usr/bin/python3 /home/jack/Downloads/r_gpio_ok_over.py &
exit 0
旋转编码器定稿程序(含正反旋转、空格按键),开机启动参见上篇
#!/usr/bin/env python
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import uinput
device = uinput.Device([
uinput.KEY_LEFTSHIFT,
uinput.KEY_TAB,
uinput.KEY_SPACE
])
RoAPin = 17 # CLK Pin
RoBPin = 18 # DT Pin
BtnPin = 27 # Button Pin
globalCounter = 0
flag = 0
BtnFlag = 0
Last_RoB_Status = 0
Current_RoB_Status = 0
Current_Btn_Status = 0
def setup():
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # Numbers GPIOs by physical location
GPIO.setup(RoAPin, GPIO.IN) # input mode
GPIO.setup(RoBPin, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(BtnPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
def rotaryDeal():
global flag
global Last_RoB_Status
global Current_RoB_Status
global globalCounter
global BtnFlag
global Current_Btn_Status
Last_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin)
while(not GPIO.input(RoAPin)): #未旋转时,GPIO.input(RoAPin)值为1,旋转时会变为0
Current_RoB_Status = GPIO.input(RoBPin) #旋转时的当前值
flag = 1
if flag == 1:
flag = 0
if (Last_RoB_Status == 1) and (Current_RoB_Status == 0):
globalCounter = globalCounter + 1 #顺时针旋转,角位移增大
device.emit_combo([uinput.KEY_LEFTSHIFT,uinput.KEY_TAB,])
if (Last_RoB_Status == 0) and (Current_RoB_Status == 1):
globalCounter = globalCounter - 1 #逆时针旋转,数值减小
device.emit_combo([uinput.KEY_TAB,])
while(not GPIO.input(BtnPin)): #未按下按钮时,GPIO.input(BtnPin)值为1,按下时会变为0
Current_Btn_Status = GPIO.input(BtnPin) #按下按钮时的当前值
BtnFlag = 1
if BtnFlag == 1:
BtnFlag = 0
device.emit_combo([uinput.KEY_SPACE])
def btnISR(channel):
global globalCounter
globalCounter = 0
def loop():
global globalCounter
tmp = 0 # Rotary Temperary
GPIO.add_event_detect(BtnPin, GPIO.FALLING, callback=btnISR)
#当按下按钮时,调用回调函数btnISR
while True:
rotaryDeal()
if tmp != globalCounter:
print('globalCounter = %d' % globalCounter)
tmp = globalCounter
def destroy():
GPIO.cleanup() # Release resource
if __name__ == '__main__': # Program start from here
setup()
try:
loop()
except KeyboardInterrupt: # When 'Ctrl+C' is pressed, the child program destroy() will be executed.
destroy()
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ouzEOft6yZ4l0St4kO_79g