树莓派开机自动运行streamlit
如果树莓派没有连接显示器,可能会出现添加了启动文件后,开机不会自动启动的问题,此时需要修改/boot/config.txt文件,
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
找到hdmi_force_hotplug=1这一行,把前面的#号删除掉创建一个服务文件:打开一个文本编辑器,创建一个新的服务文件,比如streamlit.service。
编辑服务文件:在服务文件中,输入以下内容:
[Unit]
Description=Streamlit App
[Service]
ExecStart=/home/pi/.local/bin/streamlit run /home/pi/下载/my_login_main.py
WorkingDirectory=/home/pi/下载
Restart=always
User=pi
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
请确保将/path/to/your/streamlit/app替换为你实际的Streamlit应用程序所在的路径,将your_app.py替换为你的应用程序文件名。将<your_username>替换为你的用户名。
保存服务文件:保存服务文件,并将其命名为streamlit.service。
将服务文件移动到系统服务目录:打开终端,并使用以下命令将服务文件移动到系统服务目录:
sudo mv streamlit.service /etc/systemd/system/
启用和启动服务:在终端中使用以下命令启用和启动服务:
sudo systemctl enable streamlit.service
sudo systemctl start streamlit.service
验证服务状态:使用以下命令验证服务是否正在运行:
sudo systemctl status streamlit.service
如果服务正在运行,你应该能够看到"active (running)"的状态。
请注意,这些步骤适用于基于systemd的Linux发行版,如Ubuntu。电商数据分析
为streamlit提供登录界面
准备工作
pip install streamlit-authenticator创建 YAML 文件:config.yaml
credentials:
usernames:
liba001:
email: [email protected]
name: John Smith
password: abc # To be replaced with hashed password
liba002:
email: [email protected]
name: Rebecca Briggs
password: def # To be replaced with hashed password
cookie:
expiry_days: 365
key: random_signature_key # Must be string
name: random_cookie_name
preauthorized:
emails:
- [email protected]使用 Hasher 模块将纯文本密码转换为哈希密码:
import streamlit_authenticator as stauth
hashed_passwords = stauth.Hasher(['abc', 'def']).generate()
print(hashed_passwords)将 YAML 文件中的纯文本密码替换为生成的哈希密码
开始主程序
import yaml
from yaml.loader import SafeLoader
with open('config.yaml') as file:
config = yaml.load(file, Loader=SafeLoader)
authenticator = Authenticate(
config['credentials'],
config['cookie']['name'],
config['cookie']['key'],
config['cookie']['expiry_days'],
config['preauthorized']
)
name, authentication_status, username = authenticator.login('Login', 'main')
if authentication_status:
authenticator.logout('Logout', 'main')
st.write(f'Welcome *{name}*')
st.title('Some content')
elif authentication_status == False:
st.error('Username/password is incorrect')
elif authentication_status == None:
st.warning('Please enter your username and password')streamlit参考
streamlit实时网页
import time # to simulate a real time data, time loop
import numpy as np # np mean, np random
import pandas as pd # read csv, df manipulation
import plotly.express as px # interactive charts
import streamlit as st # 🎈 data web app development
st.set_page_config(
page_title="Real-Time Data Science Dashboard",
page_icon="✅",
layout="wide",
)
# read csv from a github repo
dataset_url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Lexie88rus/bank-marketing-analysis/master/bank.csv"
# read csv from a URL
@st.experimental_memo
def get_data() -> pd.DataFrame:
return pd.read_csv(dataset_url)
df = get_data()
# dashboard title
st.title("Real-Time / Live Data Science Dashboard")
# top-level filters
job_filter = st.selectbox("Select the Job", pd.unique(df["job"]))
# creating a single-element container
placeholder = st.empty()
# dataframe filter
df = df[df["job"] == job_filter]
# near real-time / live feed simulation
for seconds in range(200):
df["age_new"] = df["age"] * np.random.choice(range(1, 5))
df["balance_new"] = df["balance"] * np.random.choice(range(1, 5))
# creating KPIs
avg_age = np.mean(df["age_new"])
count_married = int(
df[(df["marital"] == "married")]["marital"].count()
+ np.random.choice(range(1, 30))
)
balance = np.mean(df["balance_new"])
with placeholder.container():
# create three columns
kpi1, kpi2, kpi3 = st.columns(3)
# fill in those three columns with respective metrics or KPIs
kpi1.metric(
label="Age ⏳",
value=round(avg_age),
delta=round(avg_age) - 10,
)
kpi2.metric(
label="Married Count 💍",
value=int(count_married),
delta=-10 + count_married,
)
kpi3.metric(
label="A/C Balance $",
value=f"$ {round(balance,2)} ",
delta=-round(balance / count_married) * 100,
)
# create two columns for charts
fig_col1, fig_col2 = st.columns(2)
with fig_col1:
st.markdown("### First Chart")
fig = px.density_heatmap(
data_frame=df, y="age_new", x="marital"
)
st.write(fig)
with fig_col2:
st.markdown("### Second Chart")
fig2 = px.histogram(data_frame=df, x="age_new")
st.write(fig2)
st.markdown("### Detailed Data View")
st.dataframe(df)
time.sleep(1)
开机启动streamlit服务
树莓派开机启动程序的几种方式
树莓派安装配置数据库mariadb-server并建库建表插入数据
sudo apt update
sudo atp upgrade -y
sudo apt-get install mariadb-server配置
sudo mysql_secure_installation
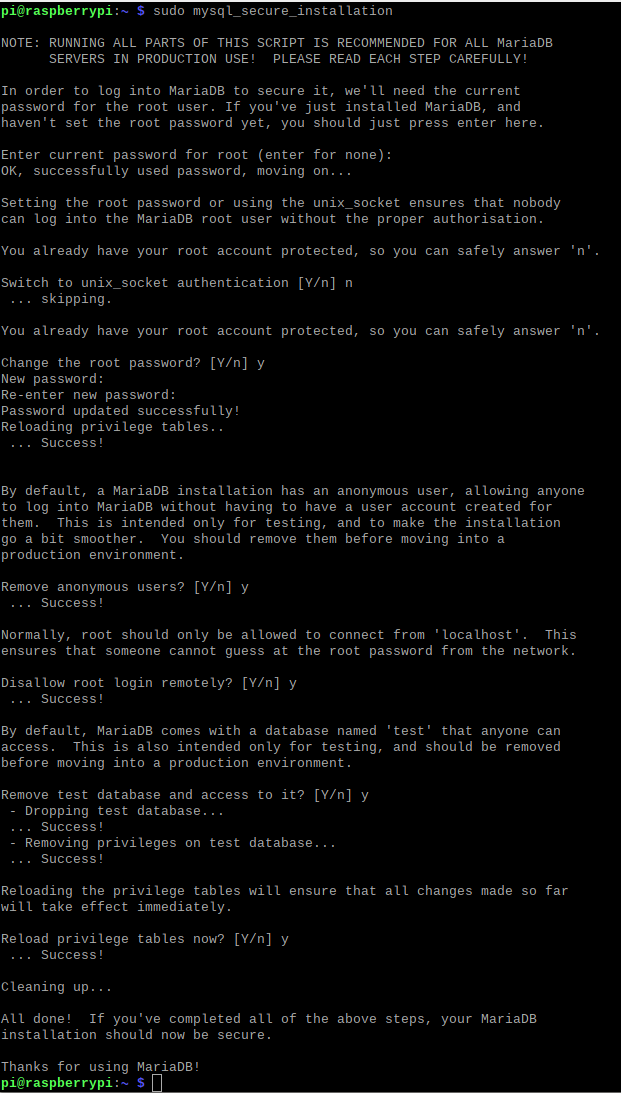
创建数据库
建库建表
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 38
Server version: 10.5.19-MariaDB-0+deb11u2 Debian 11
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> create database mydb;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> use mydb;
Database changed
MariaDB [mydb]> CREATE TABLE salesdata(
-> user_id INT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-> username VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
-> password VARCHAR(40) NOT NULL,
-> PRIMARY KEY(user_id)
-> );
MariaDB [mydb]> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mydb |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
+--------------------+
4 rows in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [mydb]>
向表格中插入数据
MariaDB [mydb]> INSERT INTO salesdata(username,password) VALUES("liba001","20252025");
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.004 sec)
MariaDB [mydb]>
查询数据
MariaDB [mydb]> select * from salesdata;
+---------+----------+----------+
| user_id | username | password |
+---------+----------+----------+
| 1 | liba001 | 20252025 |
+---------+----------+----------+
1 row in set (0.001 sec)
MariaDB [mydb]>